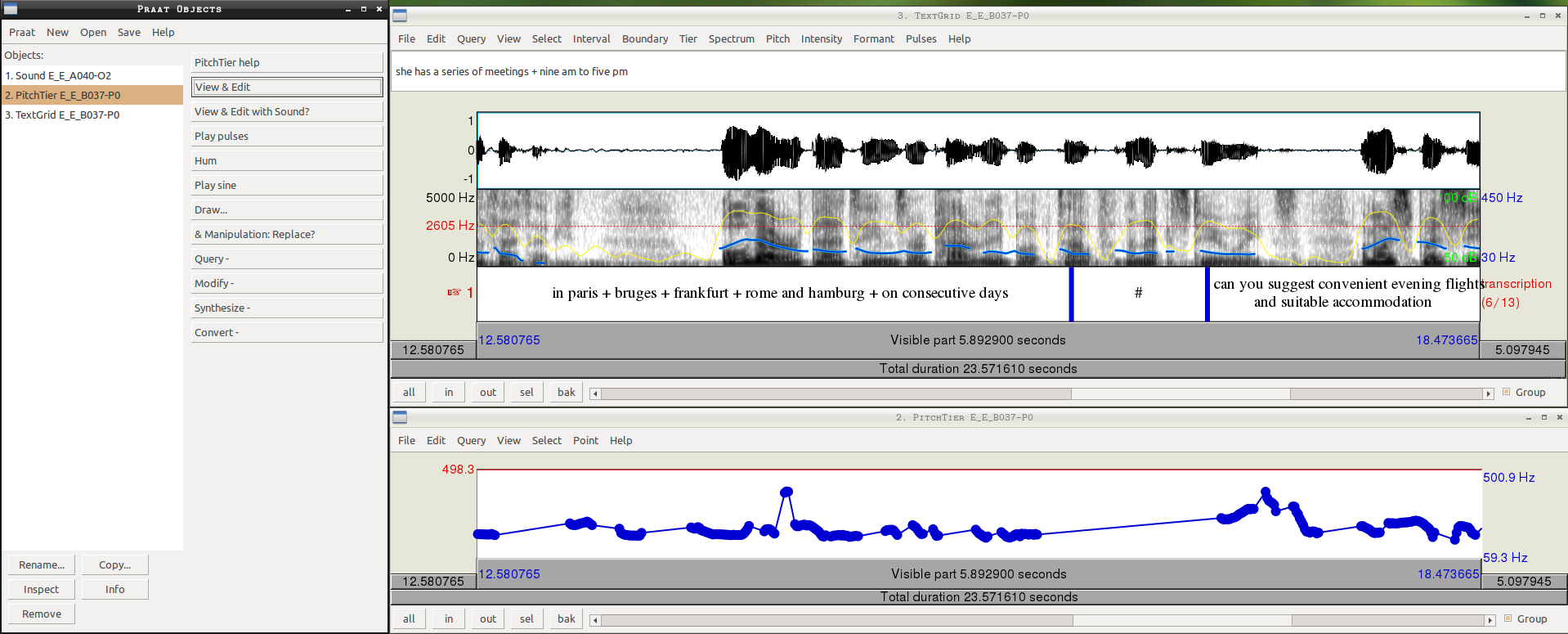
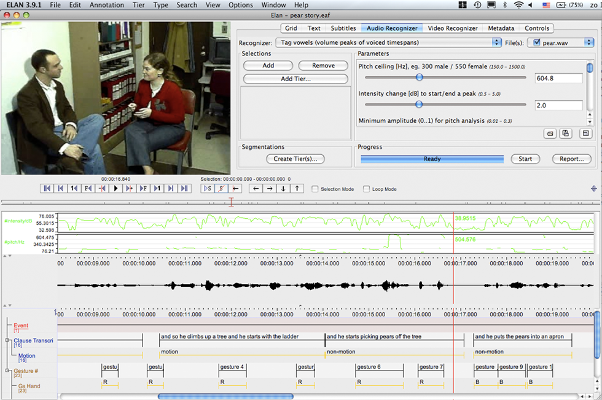
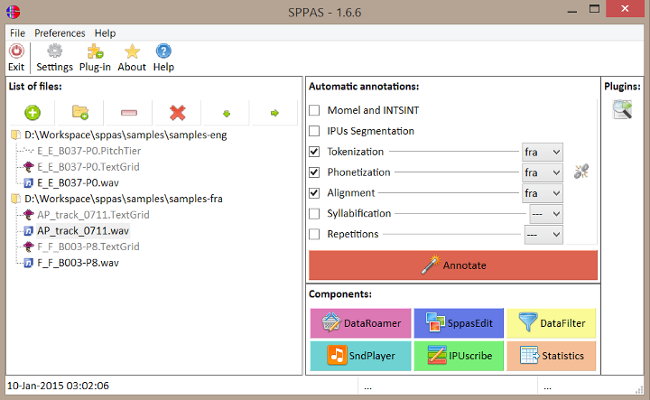
Software selection
- The choise of all annotation software must be done carefully, and before the creation of the corpus.
- It is part of the corpus creation framework.
To decide about usefulness and usability, it is necessary to know:
- about the license,
- about the ease of use,
- about the strengths/weaknesses for specific annotation purposes,
- about the type of data or analysis it is designed for,
- about its compatibility with other annotated data.
 versus
versus